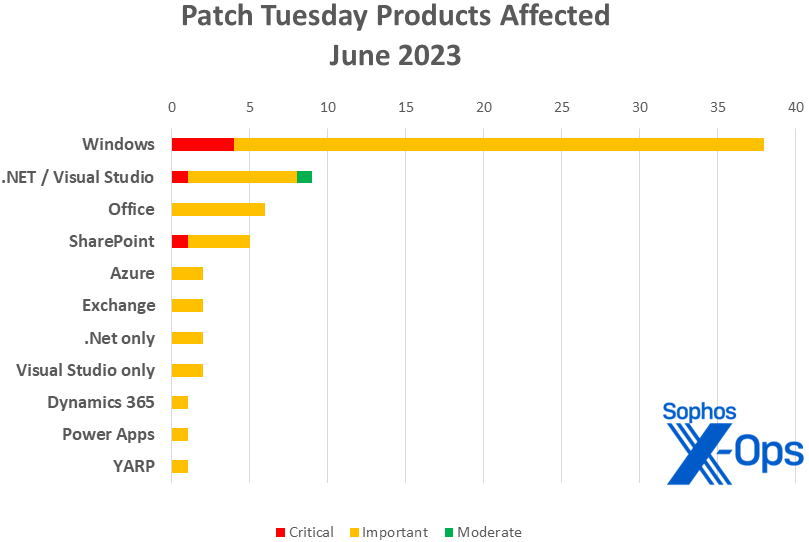
Microsoft on Tuesday released patches for 69 vulnerabilities, including four critical-severity issues in Windows and one each in SharePoint and Visual Studio / .NET. As usual, the largest number of addressed vulnerabilities affect Windows, with 38 CVEs. Patches applicable to both .NET and Visual Studio account for nine of the remainder. Office takes six patches; SharePoint, five. Azure, Exchange, .NET (without Visual Studio), and Visual Studio (without .NET) each get two. Dynamics 365, PowerApps, and YARP (Yet Another Reverse Proxy, related to .NET and NuGet) each get one.
In a heavier-than-usual month for announcements concerning patches not directly handled by Microsoft, the company is also providing information on 25 patches from Chromium (Google), GitHub, Autodesk, and… Microsoft. The situation around those 25 information-only announcements is a bit tangled. Not only are there far more than usual (and this with no Adobe patches flagged, though Adobe did release updates on its own today) but the 17 Chromium patches affecting the Edge browser hail from both Google and Microsoft itself. One of the 17, CVE-2023-3079, a V8 type-confusion issue patched by Google on June 5, is known to be under exploit in the wild. (V8 is a JavaScript engine developed by the Chromium Project and used in a variety of applications, Edge among them.)
At patch time, none of the issues this month have been publicly disclosed (aside from the information published about the info-only patches released prior to June 13). However, Microsoft cautions that eight of the issues addressed are more likely to be exploited in either the latest or earlier versions of the affected product soon (that is, within the next 30 days). Microsoft once again this month offered no guidance overview on exploitation likelihood in earlier versions versus latest versions for any of their patches.
Elsewhere on the patching scene, Fortinet this week published a security advisory for a critical-class SSL-VPN vulnerability under active exploit in the wild. CVE-2023-27997 affects FortiOS and FortiProxy SSL-VPN. A remote-code execution issue, it affects multiple versions of the software and was discovered by Fortinet’s own researchers, along with external researchers engaged in responsible disclosure, during a code audit after a previous incident. Fortinet customers are urged to review the available information and patch their devices soon; the Sophos MDR team is monitoring the situation as it unfolds.
We are including at the end of this post three appendices listing all Microsoft’s patches, sorted by severity, by predicted exploitability, and by product family. As per Microsoft’s guidance we’ll treat the three Edge patches (CVE-2023-29345, CVE-2023-33143, CVE-2023-33145) with Microsoft-assigned CVE numbers as information-only; they are not included in any of the totals or charts that follow.
By the Numbers
- Total Microsoft CVEs: 69
- Total advisories shipping in update: 0
- Publicly disclosed: 0
- Known-exploited: 0
- Severity
- Critical: 6
- Important: 62
- Moderate: 1
- Impact
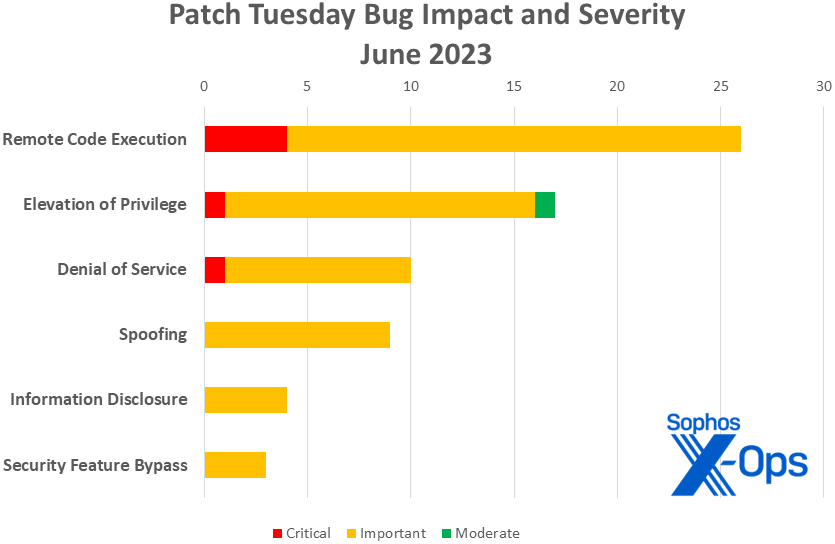
- Remote Code Execution: 26
- Elevation of Privilege: 17
- Denial of Service: 10
- Spoofing: 9
- Information Disclosure: 4
- Security Feature Bypass: 3
Figure 1: Remote code execution issues once again top the charts in June
Products
- Windows: 38
- .NET and Visual Studio: 9
- Office: 6
- SharePoint: 5
- Azure: 2
- Exchange: 2
- .NET (no Visual Studio): 2
- Visual Studio (no .NET): 2
- Dynamics 365: 1
- Power Apps: 1
- YARP: 1
In addition to the 17 Chromium / Edge patches discussed above, Microsoft also acknowledged three Autodesk-related CVEs and five GitHub-related CVEs in this month’s patch-release announcements. All eight of these issues were patched on Tuesday, and Microsoft mentions them in their own Patch Tuesday release to state that the latest version of Visual Studio is hereby protected. It’s less clear, though that older versions of Visual Studio are likewise protected; system administrators tending older systems should proceed with caution.
Figure 2: Windows accounts for more than half of June’s patches, but there are plenty to go around
Notable June updates
CVE-2023-29357 — Microsoft SharePoint Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
The only update this month with the dubious distinction of being both critical-class and more likely to be exploited in the next 30 days, this issue also sports a 9.8 CVSS base score, making it the month’s leading item of concern. According to the information available, an attacker who has gained access to spoofed JWT (JSON Web Token) authentication tokens can use them to execute a network attack which bypasses authentication and allows them to gain access to the privileges of an authenticated user — no privileges nor user action required. The bulletin takes pains to let sysadmins know they too must take pains: The fix includes multiple patches for SharePoint Foundation Server 2013, SharePoint Enterprise Server 2016, or SharePoint Server 2019, and all applicable patches have to be applied. There’s a slight silver lining for on-premises customers: If ASMI (the Advanced System Management Interface) is enabled, you’re okay.
CVE-2023-29363 — Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2023-32014 — Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2023-32015 — Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Less likely to be exploited in the next 30 days but still concerning, these three critical-class RCEs share a name and a focus on Pragmatic General Multicast, and are described similarly by the company: When Windows message queuing service is running in a PGM Server environment, an attacker could send a specially crafted file over the network to achieve remote code execution and attempt to trigger malicious code. Exploitation of any of these requires that the target system have the Windows message queuing service enabled, which may prove a mitigation for some systems.
CVE-2023-29353 – Sysinternals Process Monitor for Windows Denial of Service Vulnerability
While not particularly exciting in itself, this Important-class denial of service issue is the only one delivering its patches via the Microsoft Store this month. According to Microsoft, successful exploitation of this vulnerability requires an attacker to create the ProcMon exploit file, which is complicated. In addition, there are several aspects left to pure luck regarding how memory within ProcMon is laid out.
CVE-2023-33146 — Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
This important-class RCE involves SketchUp graphics, and Microsoft has published information on how to disable the ability to insert those in Office files while things get sorted out. Admins of Mac systems should take that advice seriously, since although the vulnerability appears to affect that platform as well as Windows, there’s not a patch yet for Microsoft Office 2019 for Mac or Microsoft Office LTSC for Mac 2021. Microsoft hasn’t given a date yet for those fixes, but says they’ll update the CVE information when it’s ready (ETA: They’re updated; time to patch).
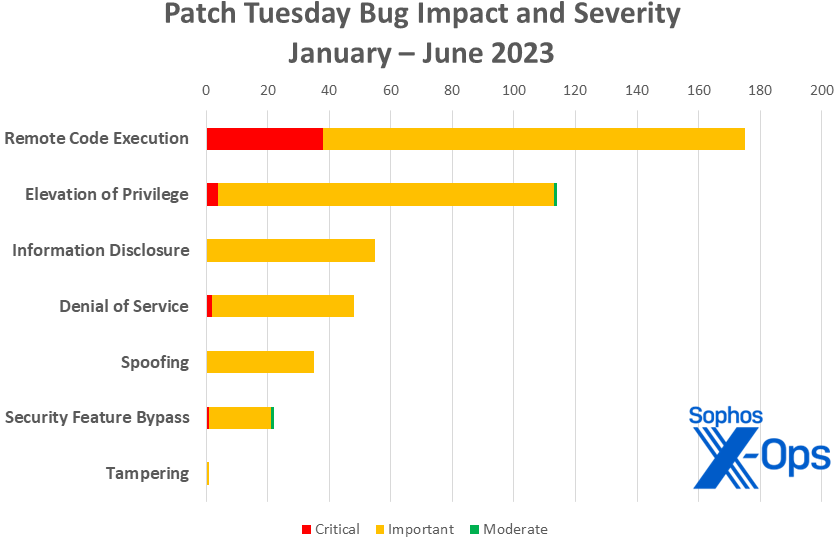
Figure 3: As we near the halfway point of the year, the overall patch count is below that of 2022 for both RCEs and EoPs; Microsoft has released 450 patches so far, compared to 487 at this point in 2022
Sophos protections
| CVE | Sophos Intercept X/Endpoint IPS | Sophos XGS Firewall |
| CVE-2023-28310 | 2308468 | 2308468 |
| CVE-2023-29357 | 2308488, 2308489, 2308490, 2308492 | 2308488, 2308489, 2308490, 2308492 |
| CVE-2023-29358 | Exp/2329358-A | |
| CVE-2023-29360 | Exp/2329360-A | |
| CVE-2023-29361 | Exp/2329361-A | |
| CVE-2023-29371 | Exp/2329371-A |
As you can every month, if you don’t want to wait for your system to pull down Microsoft’s updates itself, you can download them manually from the Windows Update Catalog website. Run the winver.exe tool to determine which build of Windows 10 or 11 you’re running, then download the Cumulative Update package for your specific system’s architecture and build number.
Appendix A: Vulnerability Impact and Severity
This is a list of June’s patches sorted by impact, then sub-sorted by severity. Each list is further arranged by CVE.
Remote Code Execution (26 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2023-24897 | .NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29363 | Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32014 | Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32015 | Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-24895 | .NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-28310 | Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29326 | .NET Framework Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29337 | NuGet Client Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29362 | Remote Desktop Client Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29365 | Windows Media Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29366 | Windows Geolocation Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29367 | iSCSI Target WMI Provider Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29370 | Windows Media Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29372 | Microsoft WDAC OLE DB provider for SQL Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29373 | Microsoft ODBC Driver Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32008 | Windows Resilient File System (ReFS) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32017 | Microsoft PostScript Printer Driver Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32018 | Windows Hello Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32029 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32031 | Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33126 | .NET and Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33128 | .NET and Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33131 | Microsoft Outlook Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33133 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33137 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33146 | Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Elevation of Privilege (17 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2023-29357 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-29346 | NTFS Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29351 | Windows Group Policy Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29358 | Windows GDI Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29359 | GDI Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29360 | Windows TPM Device Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29361 | Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29364 | Windows Authentication Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29368 | Windows Filtering Platform Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29371 | Windows GDI Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32009 | Windows Collaborative Translation Framework Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32010 | Windows Bus Filter Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32012 | Windows Container Manager Service Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32032 | .NET and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33135 | .NET and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33142 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Moderate severity | |
| CVE-2023-24936 | .NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Denial of Service (10 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2023-32013 | Windows Hyper-V Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-24937 | Windows CryptoAPI Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-24938 | Windows CryptoAPI Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29331 | .NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29353 | Sysinternals Process Monitor for Windows Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29369 | Remote Procedure Call Runtime Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32011 | Windows iSCSI Discovery Service Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32030 | .NET and Visual Studio Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33129 | Microsoft SharePoint Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33141 | Yet Another Reverse Proxy (YARP) Denial of Service Vulnerability |
Spoofing (9 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-21565 | Azure DevOps Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-21569 | Azure DevOps Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-24896 | Dynamics Finance and Operations Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32020 | Windows DNS Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32024 | Microsoft Power Apps Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33130 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33132 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33140 | Microsoft OneNote Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33144 | Visual Studio Code Spoofing Vulnerability |
Information Disclosure (4 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-29355 | DHCP Server Service Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32016 | Windows Installer Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32019 | Windows Kernel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33139 | Visual Studio Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
Security Feature Bypass (3 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-29352 | Windows Remote Desktop Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32021 | Windows SMB Witness Service Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32022 | Windows Server Service Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Appendix B: Exploitability
This is a list of the June CVEs judged by Microsoft to be more likely to be exploited in the wild within the first 30 days post-release, as well as those already known to be under exploit. Each list is further arranged by CVE.
| Exploitation more likely | |
| CVE-2023-28310 | Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29357 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29358 | Windows GDI Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29359 | GDI Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29360 | Windows TPM Device Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29361 | Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29371 | Windows GDI Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32031 | Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Appendix C: Products Affected
This is a list of June’s patches sorted by product family, then sub-sorted by severity. Each list is further arranged by CVE.
Windows (38 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2023-29363 | Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32013 | Windows Hyper-V Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32014 | Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32015 | Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-24937 | Windows CryptoAPI Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-24938 | Windows CryptoAPI Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29346 | NTFS Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29351 | Windows Group Policy Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29352 | Windows Remote Desktop Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29353 | Sysinternals Process Monitor for Windows Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29355 | DHCP Server Service Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29358 | Windows GDI Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29359 | GDI Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29360 | Windows TPM Device Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29361 | Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29362 | Remote Desktop Client Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29364 | Windows Authentication Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29365 | Windows Media Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29366 | Windows Geolocation Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29367 | iSCSI Target WMI Provider Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29368 | Windows Filtering Platform Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29369 | Remote Procedure Call Runtime Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29370 | Windows Media Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29371 | Windows GDI Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29372 | Microsoft WDAC OLE DB provider for SQL Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29373 | Microsoft ODBC Driver Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32008 | Windows Resilient File System (ReFS) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32009 | Windows Collaborative Translation Framework Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32010 | Windows Bus Filter Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32011 | Windows iSCSI Discovery Service Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32012 | Windows Container Manager Service Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32016 | Windows Installer Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32017 | Microsoft PostScript Printer Driver Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32018 | Windows Hello Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32019 | Windows Kernel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32020 | Windows DNS Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32021 | Windows SMB Witness Service Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32022 | Windows Server Service Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
NET and Visual Studio (9 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2023-24897 | .NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-24895 | .NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29331 | .NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32030 | .NET and Visual Studio Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32032 | .NET and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33126 | .NET and Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33128 | .NET and Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33135 | .NET and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Moderate severity | |
| CVE-2023-24936 | .NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Office (6 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-32029 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33131 | Microsoft Outlook Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33133 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33137 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33140 | Microsoft OneNote Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33146 | Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
SharePoint (5 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2023-29357 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-33129 | Microsoft SharePoint Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33130 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33132 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33142 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Azure (2 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-21565 | Azure DevOps Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-21569 | Azure DevOps Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
Exchange (2 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-28310 | Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-32031 | Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
.NET (no Visual Studio) (2 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-29326 | .NET Framework Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-29337 | NuGet Client Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Visual Studio (no .NET) (2 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-33139 | Visual Studio Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-33144 | Visual Studio Code Spoofing Vulnerability |
Dynamics 365 (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-24896 | Dynamics Finance and Operations Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability |
Power Apps (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-32024 | Microsoft Power Apps Spoofing Vulnerability |
YARP (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-33141 | Yet Another Reverse Proxy (YARP) Denial of Service Vulnerability |